Did you know up to 10% of women around the globe have Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)? It’s a major hormonal disorder during the fertile years. Yet, a lot of myths make it hard for millions to get the right help. Learning the truth about PCOS helps women deal with its challenges better.
Many people mix up the truth and myths about PCOS, causing unnecessary worry and stigma. A study showed doctors worry about mislabeling PCOS based on a few signs. Myths can make it hard to deal with things like irregular periods, infertility, or weight issues. We want to shine a light on PCOS facts to help women take control of their health.
Understanding the truth about ovarian cysts, fertility, and lifestyle choices helps women know more about their bodies. We’re here to clear up eight big myths about PCOS. It’s about separating the real from the false for a better way of handling this complex issue.
Key Takeaways
- PCOS affects up to 10% of women worldwide, many don’t know they have it.
- It’s easy to confuse PCOS symptoms with other issues.
- Women with PCOS go through different symptoms, needing care just for them.
- Living healthy can majorly ease PCOS symptoms.
- Talking with doctors is crucial for handling PCOS well.
Understanding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder affecting women of childbearing age. It is marked by various hormonal imbalances leading to several health issues. Despite what some believe, many women with PCOS don’t have cysts on their ovaries.
Common symptoms of PCOS include irregular periods, high androgen levels, and problems like mood swings and gaining weight. Around 10% of people with ovaries might experience PCOS, pointing to its widespread yet often overlooked presence.
PCOS extends beyond reproductive health concerns, posing risks of diabetes, heart disease, and mental health problems such as anxiety and depression. It’s crucial for those diagnosed to have regular medical check-ups to keep an eye on hormonal levels and treatment progress.
There are different types of PCOS, including lean and obese variations, each coming with its own set of challenges. Making lifestyle adjustments like eating healthily and exercising can help manage the symptoms. The medical field is continually finding better treatments and conducting research, bringing hope for those affected. For extra insights into common myths and treatment options, check out this useful site.
The Symptoms of PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) affects many with a range of symptoms. Knowing these signs is crucial for early help and better management. It helps in finding the right treatments and encourages seeking help early.
Common Symptoms to Recognize
Those with PCOS may deal with several issues like:
- Irregular menstrual cycle: This means having no periods or very long cycles.
- Hirsutism: This is when there’s too much hair in areas where men usually grow hair, like the face and chest.
- Weight gain and trouble losing it, often because of insulin resistance.
- Acne and skin problems, impacting how one looks and feels.
- Thinning hair on the head.
Identifying these signs is key since they hint at PCOS. With nearly five million women of childbearing age in the US affected, knowing and understanding PCOS is vital (source: PCOS statistics).
Long-term Health Issues Related to PCOS
PCOS also raises the risk for serious long-term health problems. Women with PCOS are more likely to face:
- Diabetes: There’s a higher chance of getting type 2 diabetes as they age.
- Heart disease: The condition’s effects and hormonal imbalance can increase heart risks.
- Both high blood pressure and cholesterol, requiring ongoing monitoring.
- Mental health challenges like depression and anxiety, often due to coping with symptoms and what people expect.
Handling these challenges means focusing on managing PCOS. Regular doctor visits are key to keep an eye on hormone levels. Although there’s no cure for PCOS, many treatments can ease symptoms and avoid PCOS complications.
Addressing Misconceptions: Common Myths About PCOS
Misconceptions about PCOS spread harmful myths, deterring people from getting proper care. It’s key to know the facts to manage debunking PCOS myths well. In the US, about 10 percent of women in their childbearing years have this hormonal issue. It leads to irregular periods, high insulin, and more androgens.
Many think PCOS only hits women over 30, but it affects girls and women of any age. Also, not everyone with PCOS has ovarian cysts. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, not just cysts. This means many women don’t know they have it. It highlights the need for better women’s health awareness.
Some people wrongly believe that only overweight women get PCOS. But, lean women can have it too. Even with a healthy lifestyle, women with PCOS face challenges. Risks like anxiety and diabetes are higher with PCOS. Individual care is critical as symptoms vary from person to person.
Learning from reliable sources helps fight PCOS stigma. Healthier diets and more exercise can help ease symptoms. For tips on lifestyle changes, check out this link: navigating PCOS effective lifestyle management tips.
Myth 1: All Women with PCOS Have Ovarian Cysts
The term “polycystic ovary syndrome” may mislead people to think all women with PCOS have ovarian cysts. However, this isn’t always true. Not every woman with PCOS has cysts on their ovaries. Some women might have cystic follicles seen on an ultrasound, but these aren’t usually painful or cancerous. It’s possible to be diagnosed with PCOS even if you don’t have any visible cysts.
The reality that ovarian cysts are not needed for a PCOS diagnosis changes how we think about this condition. About 10% of people with ovaries suffer from PCOS. This shows how widespread it is. Since PCOS comes with a range of symptoms, diagnosing it can be complicated.
- PCOS is often under-diagnosed, further perpetuating myths related to its symptomatology.
- Doctors may rely on ultrasound imaging but often utilize additional methods to confirm a PCOS diagnosis.
- Forms of PCOS may not show typical symptoms, leading to misconceptions about the condition.
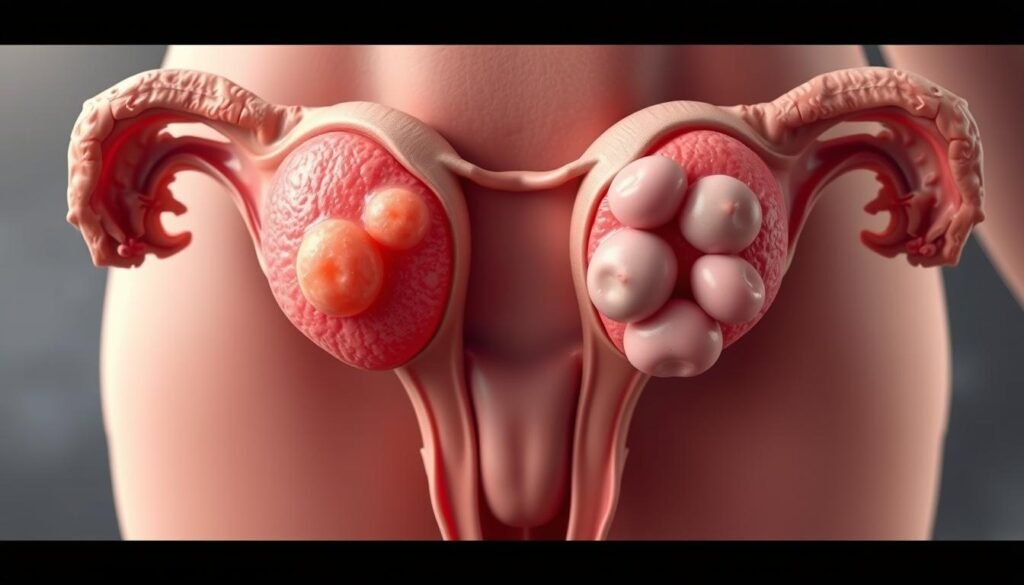
Knowing that ovarian cysts are not required for diagnosing PCOS is key. While it can be tough to manage PCOS, being informed about its signs helps people seek the right support. Understanding the myths surrounding PCOS empowers affected individuals to take charge of their well-being.
| Aspect | Fact | Myth |
|---|---|---|
| Ovarian Cysts | Not all women with PCOS have them. | All women with PCOS have cysts. |
| Diagnosis Methods | Ultrasound is just one diagnostic tool. | An ultrasound is the only way to diagnose PCOS. |
| Weight and Symptoms | PCOS can occur in individuals of any weight. | Women with PCOS are always overweight. |
Myth 2: Women with PCOS Can’t Get Pregnant
PCOS makes getting pregnant hard for many women. Yet, it’s key to know many can still have babies. Learning about treatment choices can give hope and help to those wanting to start a family.
The Truth About Fertility Challenges
For women with PCOS, getting pregnant is often tough due to irregular ovulation. Yet, it’s not impossible. About 20-30% of women with PCOS are not overweight, showing it can affect anyone.
Changing lifestyle habits can make a big difference. Eating well and exercising can balance hormones. Losing just 5-10% of weight can also make periods more regular and increase insulin sensitivity.
Fertility Treatment Options for Women with PCOS
There are many treatments for women struggling to get pregnant. These options are designed to meet their individual needs.
- Ovulation induction: Medications help the ovaries release eggs.
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI): This simple method puts sperm right into the uterus when an egg is released.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF): For those who need extra help, IVF is another step. Dr. Geetha Haripriya has helped over 27,000 women become mothers through IVF.
A caring team of healthcare professionals can design a plan to help women with PCOS have babies. They make reaching family goals attainable.
Myth 3: An Irregular Menstrual Cycle Means PCOS
An irregular menstrual cycle can worry many women. It may signal Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), but other factors also play a role. Stress, thyroid issues, and extreme dieting are other causes. It’s wrong to think an irregular cycle always means PCOS.
Around 1.55 million women of childbearing age face PCOS, but 50-70% are undiagnosed. If you have irregular cycles, see a doctor. They look into other causes of irregular cycles besides PCOS.
To diagnose PCOS, you must have two of these: high androgens, irregular cycles, or many cysts in the ovaries. Not all women with PCOS show these signs. Understanding PCOS causes and effects is vital.
- A normal menstrual cycle ranges from 21 to 35 days.
- Breastfeeding can affect menstrual regularity.
- Uterine fibroids are a common cause of menstruation changes.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease may cause irregular periods as well.
Knowing these factors helps women seek proper treatment and support. For women with PCOS, losing about 7% of weight can regulate cycles. This shows how lifestyle changes and medical advice work together.
Myth 4: Women with PCOS Can’t Lose Weight
Weight management for women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) can be tough. This is mainly because of insulin resistance. This condition affects how the body handles sugar and fat. Yet, with the right approaches, women with PCOS can still lose weight.
Understanding Insulin Resistance and Weight Management
Insulin resistance is common in women with PCOS. It makes losing weight harder for them. About 70% of women with PCOS have insulin resistance, which slows down their weight loss. Knowing about this can help in making weight loss plans that improve insulin sensitivity.
Helpful Lifestyle Modifications for Weight Loss
To lose weight with PCOS, making some lifestyle changes is key. These include:
- Regular exercise: Doing both aerobic and strength exercises helps with insulin sensitivity and losing weight.
- Healthy diet: Eating lots of whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fiber is good for weight management.
- Mindful eating: Being mindful when eating helps with choosing food and controlling portions.
Working with dietitians and fitness trainers is very helpful. They can give you tailored advice for managing PCOS weight challenges. This makes sure you get a full plan for your health.
Myth 5: All Women with PCOS Experience Unwanted Hair Growth
Not all women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) get unwanted hair growth. About one in ten women during their reproductive years face PCOS. Yet, the variability in symptoms means not all see excess hair growth. It is key to grasp how hirsutism ties to PCOS for right diagnosis and care.
Exploring Hirsutism and Its Variability
Hirsutism, or excess hair on the face, chest, back, or thighs, is a sign of PCOS. The severity of hirsutism varies by person. Your ethnicity plays a big role in this, with some groups seeing it more.
To diagnose PCOS, doctors don’t just look at hirsutism. They use a trio of clinical signs, lab tests, and ultrasound results. Two out of these three confirm the condition. This points out the variability in symptoms in PCOS cases.
| PCOS Symptoms | Commonly Associated with Hirsutism |
|---|---|
| Excessive hair growth | Yes |
| Irregular menstrual cycles | Not always |
| Acne or oily skin | Possible |
| Weight gain | Not universally |
| Difficulty conceiving | Possible, but varies |
Hirsutism is just one sign of PCOS—it doesn’t define the condition. Knowing about the variability in symptoms aids women in understanding their health better. It encourages them to seek the right treatment.

Myth 6: PCOS is Simply Caused By Poor Lifestyle Choices
Some think poor lifestyle choices are the only causes of PCOS. This view doesn’t consider the multiple elements involved in PCOS. Besides lifestyle, genetic components and hormone imbalances play a key role. Studies show hormones, insulin issues, and genetics are crucial in grasping PCOS.
About 8% to 13% of women in America deal with PCOS during their fertile years. This shows how common it is. Most of these women face insulin resistance, raising their risk of gaining weight and having metabolic problems. It’s wrong to believe every woman with PCOS is overweight, as some find gaining weight hard.
Making lifestyle improvements in diet and exercise helps with managing symptoms. But, relying only on lifestyle changes misses the full picture of PCOS. It’s important to stay healthy, yet one must see the comprehensive aspects of PCOS. This includes looking into its causes for effective support and treatment.
To wrap up, a healthier lifestyle can support women with PCOS. However, it’s crucial to see that PCOS’s roots are in genetics, hormones, and lifestyle. Knowing about all the causes of PCOS is key. This knowledge leads to better understanding and managing the condition.
Myth 7: PCOS is Reversible
There are many myths about managing PCOS, especially about curing it. People think they can totally beat this chronic issue. This leads to unfair hopes for those dealing with it. Even though we can control its symptoms with lifestyle shifts, diet, and medical help, it’s important to know PCOS always requires ongoing effort and care.
The Reality of Managing PCOS Long-Term
About 10% of women of childbearing age are affected by PCOS. Many believe they can get rid of PCOS for good. PCOS treatment options should be considered early. This proactive stance is crucial for good health.
Key strategies for managing symptoms include:
- Keeping a healthy weight, since most women with PCOS are overweight.
- Adding regular exercise and a balanced diet can help lose weight, which eases symptoms.
- Creating a personalized treatment plan with medical professionals.
Even with good symptom management, PCOS can mess with menstrual and metabolic functions. It impacts insulin resistance, cortisol levels, and inflammation, even after menopause. This shows why managing PCOS well over time is so vital.

| Component | Management Strategies | Impact on Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Weight Management | Healthy Eating, Exercise | Can alleviate symptoms significantly |
| Medical Interventions | Medications, Hormones | Helps regulate menstrual cycle |
| Ongoing Support | Therapy, Counseling | Address emotional well-being |
By setting realistic goals and pursuing comprehensive care, those with PCOS can enjoy their lives. They can control their symptoms well.
Myth 8: Birth Control Pills Cure PCOS
Many think birth control pills are a cure for PCOS. This idea is too simple for such a complex condition. Birth control can help manage PCOS symptoms but doesn’t get rid of the disease. Around 10% of people with ovaries have PCOS, which is often not diagnosed.
Doctors commonly prescribe birth control for PCOS. These pills contain estrogen and progestin. They can make menstrual cycles regular and reduce symptoms like excess hair. Yet, it’s important to see them as part of a larger PCOS management strategy.
- Birth control pills do not provide a definitive cure for PCOS.
- They assist in managing specific symptoms like irregular periods and androgen excess.
- PCOS treatment usually requires a multi-faceted approach, including lifestyle changes and possibly medication.
- Individuals should consult healthcare professionals to tailor a treatment plan for their unique symptoms.
Changing your diet and lifestyle is key to managing PCOS. Even losing a little weight can regulate menstrual cycles and boost health. exercises like high-intensity interval training are especially good for PCOS-related fat loss.
PCOS treatment needs to be customized. The condition is not just about its symptoms. Everyone’s experience with PCOS is different, highlighting the need for personalized treatment plans. While helpful for some symptoms, birth control pills are not a magic solution for PCOS.
Conclusion
It’s crucial to tackle the false beliefs about Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). This way, women can make smart health decisions. Knowing the truth about PCOS helps women find the right treatments. It also allows them to adjust their life for the better. Although PCOS may cause irregular periods and ovulation issues, many can still have babies with proper support.
Having a healthier lifestyle can also boost fertility in PCOS patients. This includes losing weight and managing insulin resistance. Supplements like Myo-Inositol and N-Acetyl Cysteine may improve hormones and ovaries. If you have symptoms, talk to a doctor for the best treatment plan.
PCOS isn’t just about having babies; it can also lead to serious health problems. This includes type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and mental health issues. Building a supportive community and focusing on research can improve how we handle PCOS. For more info, check out debunking myths about PCOS for effective management tips.