About 1 in 10 women in their child-bearing years deal with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. This disorder can mess up hormone levels. It leads to symptoms that really affect life quality. Understanding how hormone changes cause PCOS is key. It helps in handling and treating the condition effectively. Let’s dive into how these hormone changes relate to PCOS. We’ll see why knowing about this early is important.
Key Takeaways
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome affects about 10% of women in their reproductive years.
- Hormonal imbalance plays a significant role in the development of PCOS.
- This condition can lead to various symptoms including irregular periods and infertility.
- Understanding hormonal balance is crucial for managing PCOS effectively.
- Early diagnosis and intervention can improve outcomes for women with PCOS.
Understanding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex condition. It affects about 1 in 10 people of reproductive age in the United States. It often leads to hormonal abnormalities that disrupt how the body works.
Common PCOS symptoms are irregular periods, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), acne, and weight gain. These signs point to hormonal balance problems. People with PCOS may have big changes in hormones like androgens. This can make their symptoms worse.
Learning about PCOS is key to managing it. Educational resources help people understand their health. They provide tools for making wise choices. For complete information, visit essential educational materials for understanding PCOS. This knowledge helps in discussing care with doctors and in creating self-care plans.
| PCOS Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Irregular Periods | Changes in menstrual cycle duration and flow |
| Hirsutism | Excessive hair growth in unwanted areas |
| Acne | Breakouts due to hormonal fluctuations |
| Weight Gain | Difficulty maintaining a healthy weight |
What Is Hormonal Imbalance?
Hormonal imbalance happens when hormone levels in our body are not right. This can greatly affect our health. It often comes from various sources, causing hormone disruption. Key hormones like insulin, progesterone, androgens, and estrogen are crucial. They help keep the body’s systems running smoothly.
For example, insulin helps control blood sugar. Androgens are linked to male traits like muscle and bone mass.
To grasp hormonal imbalance effects, we need to value endocrine health. The endocrine system controls hormone release and balance, influencing things like metabolism, growth, and mood. A glitch in this system can trigger health issues. This includes conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Keeping an eye on hormone levels is vital for preventing problems and ensuring good health.
Tackling hormonal imbalances often means changing your lifestyle or getting medical help. Sometimes, it’s both. For deeper insights on disorders tied to hormonal imbalance, check out UpToDate. Knowing more about hormonal imbalances can help individuals actively manage their health.
Hormonal Imbalance Contributes to PCOS
Hormonal imbalance plays a big role in PCOS. Estrogen and progesterone help control the menstrual cycle. When they’re out of balance, it can cause problems like irregular periods and issues with ovulation. Knowing how these hormones work together helps us understand PCOS better.
Role of Hormones in Menstrual Regulation
Estrogen and progesterone levels change during the menstrual cycle. This helps with ovulation and keeps the uterus healthy. But, when there’s an imbalance, it can mess up the cycle.
Many women with PCOS have irregular cycles. Their cycles might last longer than 35 days or not happen at all. This is a major sign of hormonal imbalance and is crucial for understanding PCOS.
Impact on Ovulation
Women with PCOS often have trouble ovulating. This is due to irregular hormone release. Not being able to ovulate regularly can make getting pregnant hard.
Knowing about these hormonal effects is important. It helps women with PCOS manage their reproductive health. They need good strategies to deal with these imbalances.
Insulin Resistance and Its Connection to PCOS
Insulin resistance is key in the growth and worsening of PCOS. It often starts from genetic factors, a poor diet, and not moving enough. This makes the body less good at reacting to insulin. That leads to higher insulin levels, which can make hormonal imbalance worse.
This imbalance adds to the problems faced by those with PCOS.
How Insulin Resistance Develops
Many things cause insulin resistance. Important factors include:
- Genetics: A family history can make you more likely to get metabolic disorders.
- Diet: Eating lots of calories and sugar can overload your insulin processing.
- Obesity: Being overweight is closely linked to worse insulin sensitivity.
- Lack of physical activity: Not being active can lead to weight gain and hurt insulin receptors.
Effects on Ovarian Function
Insulin resistance affects how the ovaries work. High insulin can make the ovaries make too many androgens. This messes up the hormone balance needed for ovulating right.
This hormone problem can lead to:
- Irregular menstrual cycles: Not ovulating becomes common, making getting pregnant hard.
- Ovarian cyst formation: Fluid sacs can form, possibly causing more issues.
- Increased risk of infertility: It may be hard to get pregnant because the ovaries aren’t working right.
Knowing how insulin resistance, hormonal imbalance, and ovarian function are linked shows why managing is vital. Changing your lifestyle by eating right and exercising can greatly help. These changes can make your insulin reaction better and lower PCOS symptoms. For more on PCOS, visit this resource.
Androgen Excess: A Key Player in PCOS
Androgen excess is often a key factor when looking at hormonal issues in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). These male hormones are found in everyone but at different levels. For women, while important for many bodily functions, having too much can cause problems.
Understanding Androgens
Androgens, like testosterone, help with muscle growth, strong bones, and hair regulation. Women usually make these hormones. But, when there’s too much, it can upset the balance that controls periods and ovulation.
Symptoms Associated with Androgen Excess
Many symptoms make it clear when there’s too much androgen. This is crucial for diagnosing PCOS. Women with high androgen might see:
- Hirsutism: Unwanted facial and body hair growth.
- Acne: More oil production and breakouts.
- Male-pattern baldness: Losing hair like men do.
- Irregular periods: Missed or longer menstrual cycles.
Spotting these symptoms helps doctors figure out PCOS. Then, they can find the best ways to help those dealing with this hormonal imbalance.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Hirsutism | Excessive hair growth in areas typical for men, such as the face and chest. |
| Acne | Skin condition due to hormonal fluctuations leading to breakouts. |
| Male-pattern baldness | Thinning of hair on the scalp, mirroring patterns seen in males. |
| Irregular periods | Cycles that vary in length, often skipping months. |
The Presence of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are often linked with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). They form due to a hormonal imbalance that affects ovulation. The ovaries might create too many follicles, leading to multiple cysts. Understanding this hormonal issue is key for diagnosing PCOS.
Women with ovarian cysts might face challenges, especially with fertility. Having many cysts can mess with the hormones needed for ovulation. This can cause irregular periods or make getting pregnant hard. Finding these cysts via ultrasound is vital for diagnosing PCOS.
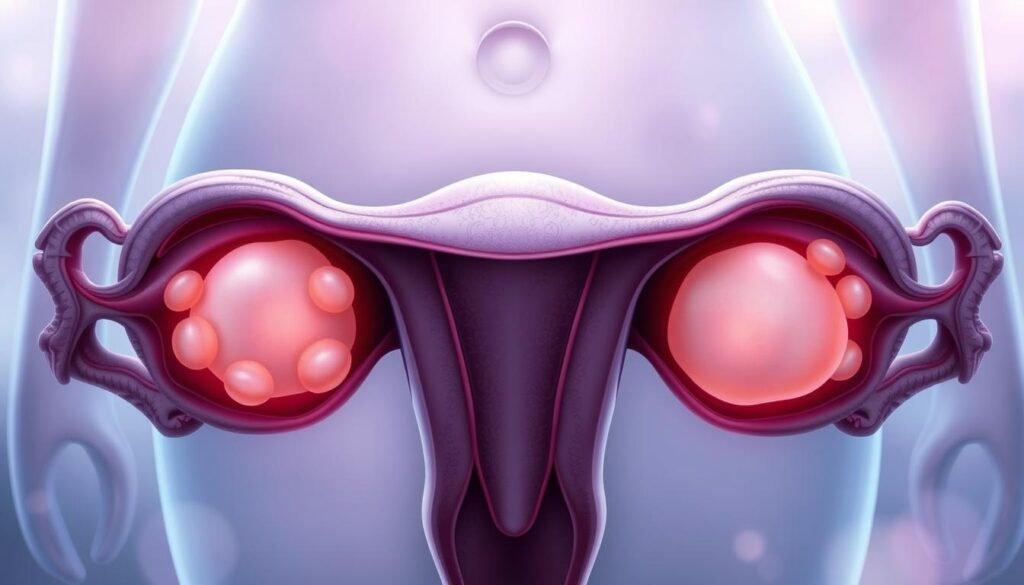
Knowing the link between ovarian cysts and hormonal imbalance is critical. It helps us connect to the symptoms and possible treatments. These treatments aim to fix hormonal balance and help with ovulation.
| Aspect | Ovarian Cysts | PCOS Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|
| Cyst Formation | Result from hormonal imbalance | Characterized by multiple cysts and hormonal disruption |
| Symptoms | May include pelvic pain | Irregular periods, weight gain, hirsutism |
| Impact on Fertility | Can hinder normal ovulation | May cause difficulties in conceiving |
| Diagnostic Methods | Ultrasound examination | Ultrasound and hormonal assessment |
Irregular Periods: A Common Symptom
Irregular periods are a major sign of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Women with this issue see their cycles change a lot. This can make them worry. Normally, a menstrual cycle is between 21 and 35 days. But PCOS can mess with this cycle.
It’s important to know what irregular periods look like. They can be:
- Cycles longer than 35 days
- Cycles that skip months
- Cycles shorter than 21 days
Many women with PCOS deal with these irregular cycles. This problem is due to hormonal imbalances. These imbalances can stop the normal process of the reproductive system. They might cause the body to make too many androgens. This can stop ovulation, leading to unpredictable periods.
Irregular periods are more than just an annoyance. They can cause reproductive health issues like infertility. This happens because such irregularities can stop you from being able to have a baby. Fixing the hormonal imbalances can help manage PCOS. It can improve reproductive health.
| Type of Menstrual Cycle | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular | Cyclic changes that occur every 21 to 35 days. |
| Irregular | Cycles longer than 35 days, shorter than 21 days, or missed entirely. |
| Oligomenorrhea | Infrequent menstrual periods, occurring less than six times a year. |
| Amenorrhea | Total absence of menstruation for three or more months. |
Knowing about irregular periods can help catch PCOS early. This leads to better ways to handle it. Paying attention to these signs means better health for women with PCOS.
Infertility Linked to Hormonal Issues
Many women with PCOS struggle with infertility because of hormonal imbalance. This imbalance blocks normal ovulation, making it hard to get pregnant. Knowing how hormones affect fertility gives hope to those trying to have a baby.
Exploring the Impact of Hormonal Balance on Fertility
Studies show fixing hormonal balance is key to better fertility in women with PCOS. Treatments and lifestyle changes can help. They target the hormone issues common with PCOS.
It’s also important to find and manage these problems early. This helps in fighting infertility caused by hormones. Women can learn a lot from resources about their condition and treatments. For more details, read the studies here about hormones and fertility.

Obesity and PCOS: A Complicated Relationship
Understanding how obesity and PCOS are connected is key for affected women. Obesity can make PCOS symptoms worse. This makes it a cycle where hormone issues get more noticeable. Diet and exercise are vital to handle these problems.
The Role of Weight in Hormonal Imbalance
Being overweight often leads to insulin resistance, which is common in PCOS. This can cause more androgens to be made, leading to more hormone issues. Then, PCOS symptoms like missed periods and excess hair might get worse.
Managing weight well can really help balance hormones. It’s important to eat well and stay active. This helps control weight and eases PCOS symptoms.
| Factor | Impact of Obesity |
|---|---|
| Insulin Resistance | Increased severity of insulin resistance in women with obesity |
| Androgen Levels | Elevated androgen production leading to worsened symptoms |
| Menstrual Regulation | Higher chances of irregular menstrual cycles |
| Fertility | Potential challenges in achieving pregnancy |
Effective interventions are crucial, as said by health professionals. They often suggest plans made just for you. These plans mix diet changes with more activity to get good results.
Managing Hirsutism in PCOS Patients
Women with PCOS facing hirsutism deal with big challenges. They need varied methods to manage it effectively. This includes lifestyle changes for a hormonal balance, like eating healthy and exercising regularly.
Medicine plays a big role in controlling hormones. Options include birth control pills, which regularize periods and lower androgen levels. Another option is anti-androgen drugs, like spironolactone. They help slow down hair growth by blocking androgens on hair follicles.
There are also cosmetic solutions for the physical side of hirsutism. Laser hair removal and electrolysis are good long-term choices for getting rid of unwanted hair. These methods can boost confidence and life satisfaction.
Handling hirsutism’s mental and cultural impacts is crucial too. Support groups and counseling offer big help here. They help women deal with the emotional side of hirsutism. This approach gives a complete understanding of managing hirsutism in PCOS.

| Management Option | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle Changes | Incorporating a balanced diet and regular exercise | Varies by individual; often beneficial for overall health |
| Hormonal Contraceptives | Regulate menstrual cycles and lower androgen levels | Highly effective for many women |
| Anti-Androgens | Block androgen receptors to reduce hair growth | Effective, but may take time to show results |
| Laser Hair Removal | Long-term solution for unwanted hair | Generally effective; results may vary based on hair type |
| Electrolysis | Permanent hair removal by damaging hair follicles | Effective; requires multiple sessions |
Conclusion
Understanding hormonal imbalance is key to managing PCOS better. Insulin resistance, high androgen levels, and obesity worsen symptoms for many women. Knowing these factors is crucial for tackling the condition effectively.
More awareness and well-rounded strategies can improve life for those with PCOS. It’s important to keep pushing for research and better treatments. These should focus on the unique hormonal challenges in PCOS.
Women should have the info and support they need for their health. With the right management plans, they can deal with PCOS symptoms more confidently. This approach helps women face their health challenges with strength.